class: center, middle, inverse, title-slide # Week 06 - Measurement ## Correlations, QQ Plots and Matrices <html> <div style="float:left"> </div> <hr color='#EB811B' size=1px width=800px> </html> ### Danilo Freire ### 25th February 2019 --- <style> .remark-slide-number { position: inherit; } .remark-slide-number .progress-bar-container { position: absolute; bottom: 0; height: 6px; display: block; left: 0; right: 0; } .remark-slide-number .progress-bar { height: 100%; background-color: #EB811B; } .orange { color: #EB811B; } </style> # Today's Agenda .font150[ * Assignments * Recap: Z-Score and Correlations * Logarithmic Transformations * Quantile-Quantile (QQ) Plots * Basic Matrix Operations ] --- # Assignments .font150[ * Late assignments * 3-4 groups missing * Assignment 3 is online - due next Monday * Research topics due next week * Please download the [Rmd file with the in class exercise](https://pols1600.github.io/slides/week06b/partner-violence.Rmd) before Wednesday ] --- # Recap .font150[ * .orange[Z-Score:] number of standard deviations an observation is above or below the mean * `\(z_{x_i} = \frac{x_i - \bar{x}}{S_x}\)` * .orange[Correlations:] the average product of the z-score of _x_ and the z-score of _y_ * `\(r_{x,y} = \frac{1}{n-1} \sum^{n}_{i=1} \big(\frac{x_i - \bar{x}}{S_x} \times \frac{y_i - \bar{y}}{S_y}\big)\)` * From -1 to +1, regardless of the original scale * Correlations only measure _linear_ relationships ] --- # The Health and Wealth of Nations ```r library(gapminder) names(gapminder) ``` ``` ## [1] "country" "continent" "year" "lifeExp" "pop" "gdpPercap" ``` ```r cor(gapminder$gdpPercap, gapminder$lifeExp) ``` ``` ## [1] 0.5837062 ``` ```r cor(gapminder$pop, gapminder$lifeExp) ``` ``` ## [1] 0.06495537 ``` ```r df <- subset(gapminder, select = c("lifeExp", "pop", "gdpPercap")) # variables cor(df, use = "pairwise.complete.obs") # pairwise correlations ``` ``` ## lifeExp pop gdpPercap ## lifeExp 1.00000000 0.06495537 0.58370622 ## pop 0.06495537 1.00000000 -0.02559958 ## gdpPercap 0.58370622 -0.02559958 1.00000000 ``` --- # The Health and Wealth of Nations ```r plot(gapminder$gdpPercap, gapminder$lifeExp, main = "GDP per capita and life expectancy", ylab = "Life expectancy", xlab = "GDP per capita", pch = 16, col = "grey") ``` <img src="week06a_files/figure-html/unnamed-chunk-2-1.png" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- # Log Transformations .font150[ * When data are skewed, we often .orange[log transform] the variable * Logarithm of a positive number _x_ is the exponent of a base _b_ * `\(y = log_{b}x \Longleftrightarrow x = b^y\)` * `\(4 = log_{3}81 \Longleftrightarrow 81 = 3ˆ{4}\)` ```r log(81, base = 3) ``` ``` ## [1] 4 ``` ] --- # Système International d'Unités (SI) .center[ | Prefix | Decimal | Base 10 | |:------:|:----------:| :------:| | giga | 1000000000 | 10^9 | | mega | 1000000 | 10^6 | | kilo | 1000 | 10^3 | | - | 1 | 10^0 | | centi | 0.01 | 10^-2 | | mili | 0.001 | 10^-3 | ] .font120[ * .orange[Logarithmic scales represent an equal amount of multiplicative change] * One log increase represents a 10x increase in the original unit * From one kilobyte (kB) to one megabyte (MB) = 1000x = just 3 in base 10 * _Pulls small values apart and bring large values together_ ] --- # Euler's Number .font150[ * Natural logarithm: `\(e\)` (Euler's number) as base value * `\(e = 2.7182 \dots\)` * `\(y = log_{e}x \Longleftrightarrow x = e^y\)` ```r log(81) # e is the base argument default ``` ``` ## [1] 4.394449 ``` ] --- # Log Transformation ```r hist(gapminder$gdpPercap, main = "GDP per capita", freq = FALSE) ``` <img src="week06a_files/figure-html/unnamed-chunk-5-1.png" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- # Log Transformation ```r hist(log(gapminder$gdpPercap), main = "Log GDP per capita", freq = FALSE) ``` <img src="week06a_files/figure-html/unnamed-chunk-6-1.png" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- # The Health and Wealth of Nations ```r plot(gapminder$gdpPercap, gapminder$lifeExp, main = "GDP per capita and life expectancy", ylab = "life expectancy", xlab = "GDP per capita", pch = 16, col = "grey") ``` <img src="week06a_files/figure-html/unnamed-chunk-7-1.png" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- # The Health and Wealth of Nations ```r cor(log(gapminder$gdpPercap), gapminder$lifeExp) ``` ``` ## [1] 0.8076179 ``` ```r plot(log(gapminder$gdpPercap), gapminder$lifeExp, main = "Log GDP per capita and life expectancy", ylab = "life expectancy",xlab = "Log GDP per capita", pch = 16, col = "grey") ``` <img src="week06a_files/figure-html/unnamed-chunk-8-1.png" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- # Log Transformations .font150[ * Often used with population or GDP per capita * Reduce positive skew * Make distributions more symmetrical * Useful because correlations are only valid for linear relationships * .orange[Always plot your data before the analysis] ] --- # Quantile-Quantile Plots .font150[ * Specific type of correlation * Compare whole distributions * Each point represents same quantile * If 2 distributions are identical, the graph will be a 45-degree line * `qqplot()` ] --- # Quantile-Quantile Plots ```r qqplot(gapminder$gdpPercap, gapminder$lifeExp, main = "QQ plot", xlab = "GDP per capita", ylab = "Life expectancy") ``` <img src="week06a_files/figure-html/unnamed-chunk-9-1.png" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- # Quantile-Quantile Plots ```r qqplot(log(gapminder$gdpPercap), gapminder$lifeExp, main = "QQ plot", xlab = "Log GDP per capita", ylab = "Life expectancy") ``` <img src="week06a_files/figure-html/unnamed-chunk-10-1.png" style="display: block; margin: auto;" /> --- # Always Plot Your Data .center[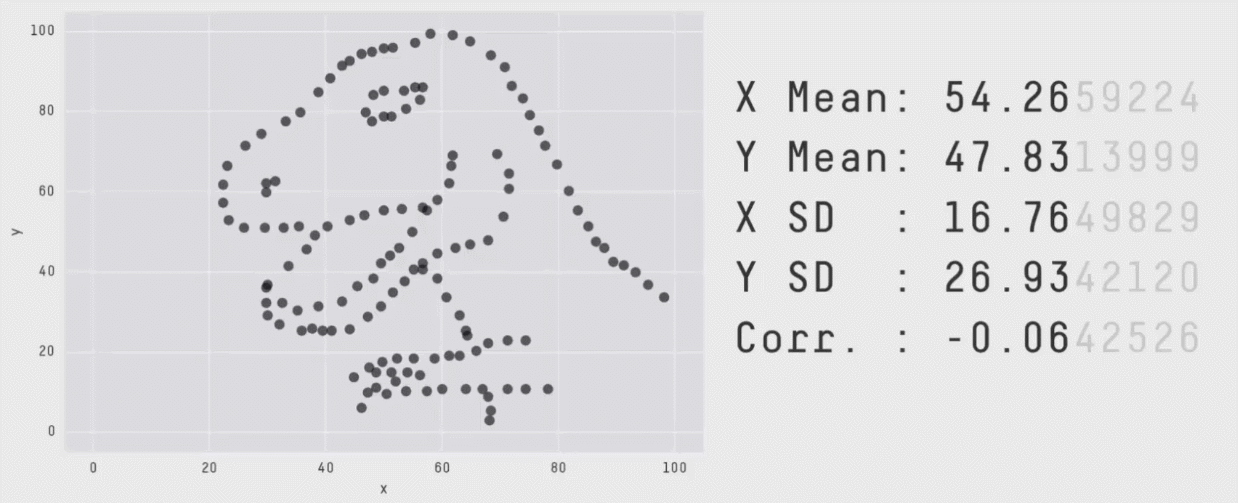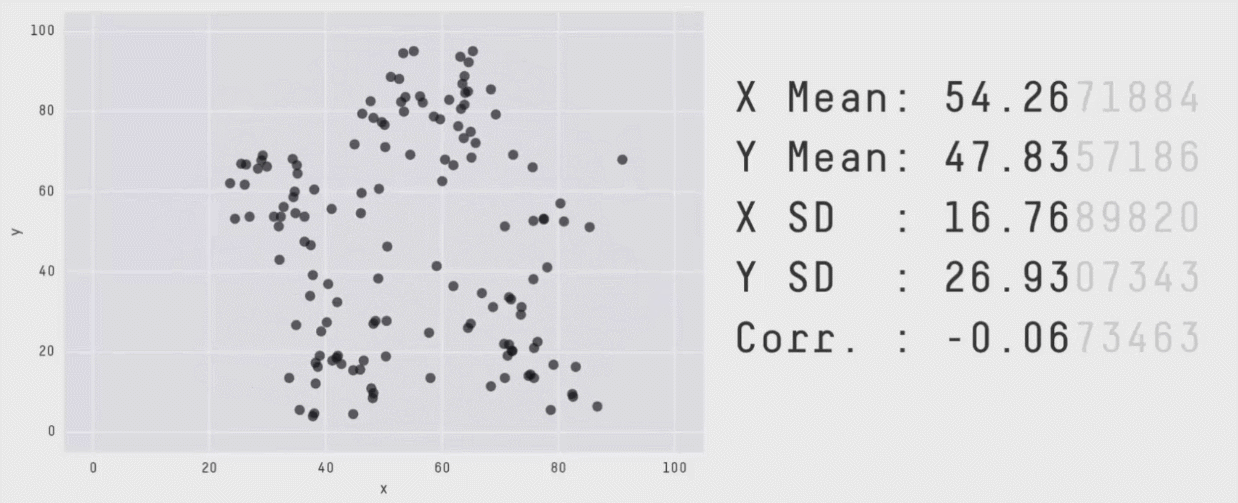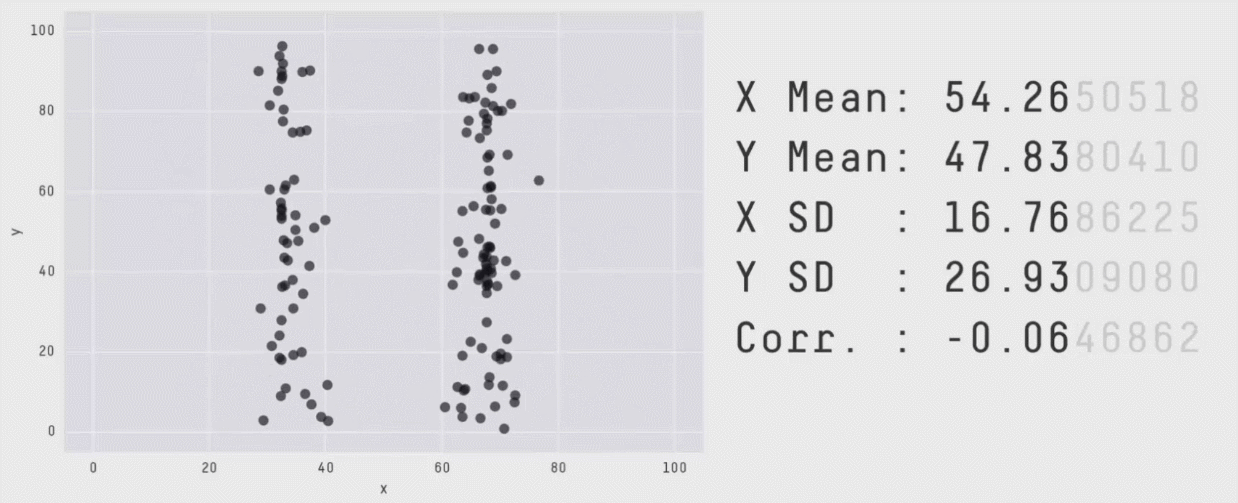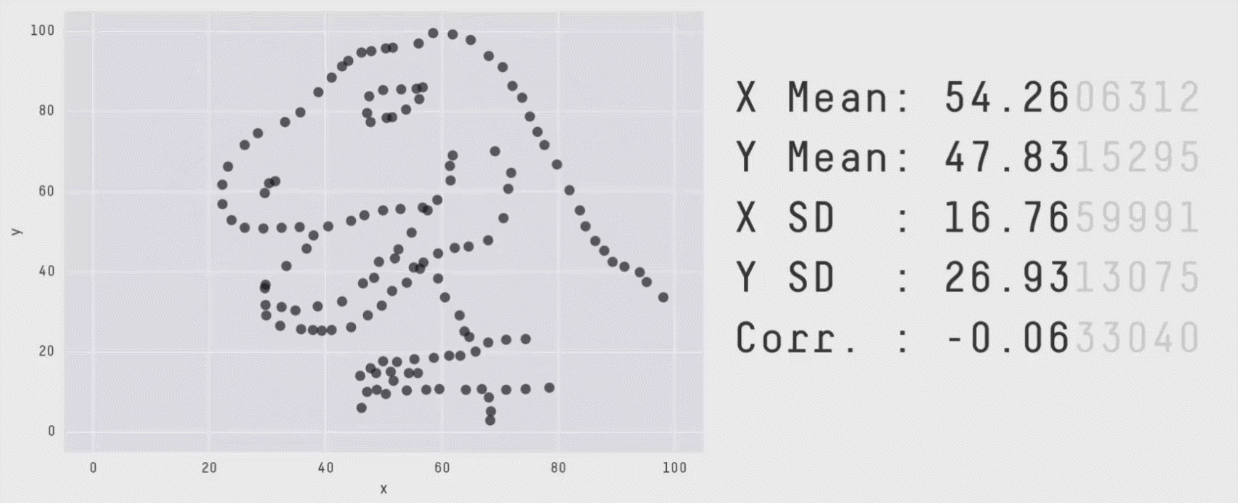] Source: [Autodesk Research](https://www.autodeskresearch.com/publications/samestats) --- class: inverse, center, middle # Questions? <html><div style='float:left'></div><hr color='#EB811B' size=1px width=720px></html> --- # Matrices .font150[ * R can perform many operations with matrices * Data frames have many types of variables (numeric, factor, integer), matrices only take numeric entries * Select variables: - Data frame: `dataset$variable` - Matrices: `matrix[row number,column number]` * `matrix(numbers, nrow = x, ncol = y, byrow = TRUE/FALSE)` ] --- # Matrices ```r ma1 <- matrix(1:10, nrow = 2, ncol = 5, byrow = TRUE) ma1 ``` ``` ## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] ## [1,] 1 2 3 4 5 ## [2,] 6 7 8 9 10 ``` ```r ma1 * 3 ``` ``` ## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] ## [1,] 3 6 9 12 15 ## [2,] 18 21 24 27 30 ``` ```r t(ma1) # transpose ``` ``` ## [,1] [,2] ## [1,] 1 6 ## [2,] 2 7 ## [3,] 3 8 ## [4,] 4 9 ## [5,] 5 10 ``` --- # Matrices ```r ma1 ``` ``` ## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] ## [1,] 1 2 3 4 5 ## [2,] 6 7 8 9 10 ``` ```r diag(ma1) # diagonal ``` ``` ## [1] 1 7 ``` ```r apply(ma1, 1, mean) # 1 = row, 2 = column ``` ``` ## [1] 3 8 ``` ```r apply(ma1, 1, sum) # sum of matrix rows ``` ``` ## [1] 15 40 ``` ```r apply(ma1, 2, sd) # standard deviation of columns ``` ``` ## [1] 3.535534 3.535534 3.535534 3.535534 3.535534 ``` --- # Matrices ```r ma2 <- matrix(21:30, nrow = 2, ncol = 5, byrow = FALSE) ma2 ``` ``` ## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] ## [1,] 21 23 25 27 29 ## [2,] 22 24 26 28 30 ``` ```r ma1 + ma2 ``` ``` ## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] ## [1,] 22 25 28 31 34 ## [2,] 28 31 34 37 40 ``` ```r ma3 <- rbind(ma1, ma2) # concatenate rows, use cbind to aggregate columns ma3 ``` ``` ## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] ## [1,] 1 2 3 4 5 ## [2,] 6 7 8 9 10 ## [3,] 21 23 25 27 29 ## [4,] 22 24 26 28 30 ``` --- # What You Have Learned .font150[ * Survey sampling: random and quota sampling * Biases: individual non-response, item non-response, social desirability * Plots: histograms, bar plots, box plots, scatter plots, time series * Z-Scores, correlations, quantile-quantile plots, list experiments ] --- # Homework .font150[ * Watch this video about Euler's number: <https://youtu.be/AuA2EAgAegE> * Start working on assignment #3 * Think of possible topics you would like to know more about ] --- class: inverse, center, middle # See You on Wednesday! <html><div style='float:left'></div><hr color='#EB811B' size=1px width=720px></html>